Updated October 23, 2019 by Siobhan Climer
Originally Published October 24, 2016
All across the technology industry, developers and tech enthusiasts are trumpeting hyperconvergence for its simplicity, ease of management, and cost savings over traditional data center architectures. With a closer look, it’s easy to see how the benefits of hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) have made this solution so appealing.
Traditional converged infrastructure, which we will discuss briefly below, is typically slow and expensive to upgrade and maintain. With the advent of 5G and edge computing, typical infrastructure will be unable to keep up. The influx of IoT – the fact that employees are likely accessing the network from multiple devices and multiple locations – means traditional converged infrastructure particularly outdated.
Hyperconvergence does something even more than increase speeds and feed. What makes HCI unique is that it aligns information technology infrastructure with broader business sentiments, such as agility and ROI.
While improving IT infrastructure management is certainly a goal, HCI enables something far more comprehensive, that appeals to the entire C-suite – from the CIO to the CFO. There is a need in the market for a cost effective solution that can keep a business nimble enough to compete despite the constant shift of new technology and changing factors.
What is Hyperconvergence Or Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI)?
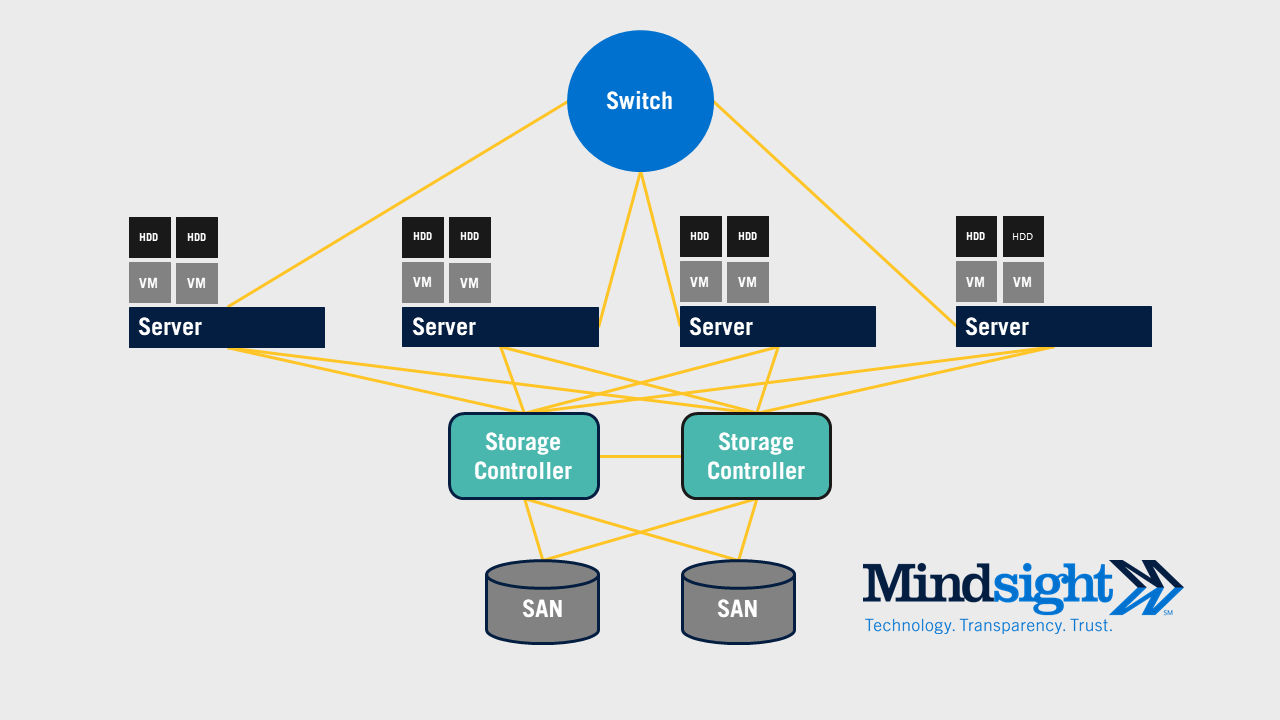
To understand what hyperconvergence is and why it is beneficial, you must first understand traditional data center design to see how it compares. In a standard data center today, a switch will route traffic to a collection of servers that house virtual machines on hypervisors. Then, these servers must access the storage area network (SAN) through the storage controller to retrieve or store any relevant data.
When server virtualization was developed, we saw a drastic reduction in the amount of equipment used in the average data center. This consolidated the data center from a sprawling series of servers to something more manageable. HCI is the next step in this consolidation trend.
The average data center architecture will resemble something like this.
Figure 1: Converged Infrastructure/Traditional Data Center Architecture
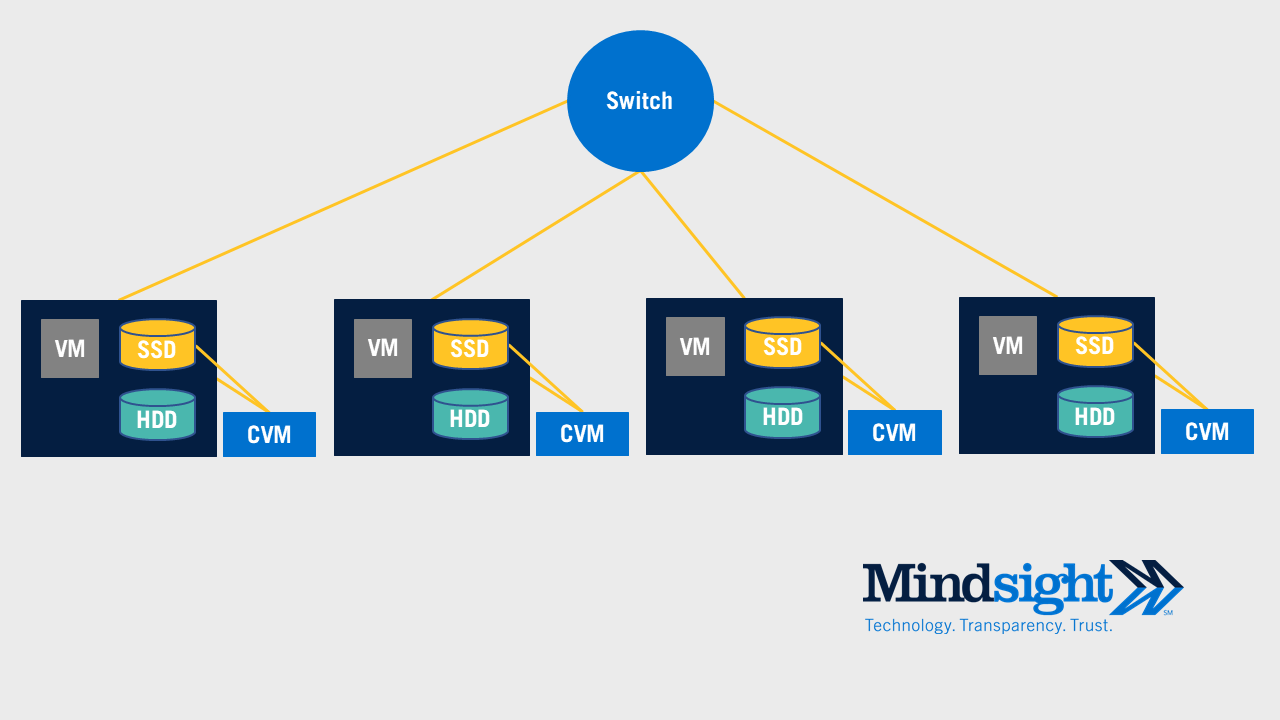
Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI), by comparison, will look like this.
Figure 2: Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) showing hyperconvergence
Hyperconverged Infrastructure: A New Approach
As you can see, hyperconvergence is a drastically different approach to a data center. It removes the SAN completely. The hypervisor, server, and storage are now all fused into a single appliance called a node. To scale the solution, you just need to deploy additional nodes.
In the design, you’ll notice that the hyperconvergence solution includes both a solid state drive (SSD) and a hard disk drive (HDD), but this may vary by developer. There are even all flash hyperconvergence solutions on the market today.
Finally, hyperconvergence is sometimes described as the software defined data center (SDDC), because a hyperconverged infrastructure is managed centrally by a single piece of software. Storage, compute, and the virtual machines are all managed by that same application.

Besides consisting of less physical equipment, hyperconvergence provides a number of important benefits to the IT environment and the business as a whole.
1) Software-defined storage: Storage in a hyperconverged infrastructure is software-defined. The storage nodes act as one highly-reliable and redundant pool of storage. Should one node go down, the rest will remain unaffected. This resilience is key to ensuring connectivity and uptime.
2) Agility: In a hyperconverged infrastructure, your workloads all fall under the same administrative umbrella. This makes it easier to migrate workloads from one location to another.
3) Scalability: Because of the node-based architecture, it is very easy to scale up your hyperconverged data center. Simply add or subtract nodes to match your resource demand. Of course, unlike dHCI, you also need to add and substract storage in a linear fashion. Learn more about dHCI, or disaggregated hyperconverged infrastructure in our recent article.
4) Data protection: HCI gives an organization the ability to easily restore data. As cybercriminal activity rises and businesses of every size become at risk of an attack, HCI embeds elements of disaster recovery and backups into your infrastucture.
5) Cost efficiency: Hyperconvergence brings an affordable economic model to any IT department. Since there is less equipment to purchase, maintain, and support, the recurring costs of supporting an HCI data center are lower.
By delivering virtualization, storage, compute, network, management and data protection in an easy to manage yet scalable application, an organization can seamlessly manage their complex infrastructure. HCI has already gained a significant foothold in the infrastructure market; the evolution of the Gartner Magic Quadrant for HCI provides this insight. It will remain a pivotal architecture for organizations of all sizes. Not only is it cost effective, but it plays a very important role in managing a company’s infrastructure.
HCI Use Cases
Consolidating the Data Center
The first and most obvious use case is consolidating the data center. In the HCI model, the SAN is gone entirely. Along with it goes any storage controllers and the entire storage array. In its place is the compact hyperconverged appliance. If data consolidation is a priority, hyperconvergence is a clear solution.
 Deploying a Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
Deploying a Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
One of the major advantages of hyperconvergence is its ability to non-disruptively scale by adding new nodes. In a VDI deployment, this can be a major benefit. Instead of overprovisioning as your company and VDI applications grow, a hyperconverged data center can layer on new nodes as the need arises.
Furthermore, the lack of a SAN removes the possibility of storage bottlenecks. The storage arrays are physically connected to the servers running the VDI application.
Performing Testing and Development
Hyperconvergence makes it easy to create logical separations for a testing and development environment. This both prevents the development team from creating a Shadow IT environment in the public cloud as well as empowers them to use best-of-breed equipment for their development needs.
Remote Management
If a portion of your team is not located on-site, data center management can prove a serious challenge. In HCI, the data center in its entirety can be managed remotely from the same central portal. This greatly improves the management of the data center.
Moving Forward
Though HCI appears on all levels to be a viable new approach to data center design, it does have its drawbacks that need to be weighed against its benefits. One of the potential issues with hyperconvergence is that it unifies the data center under a single vendor.
In addition, unlike disaggregated hyperconverged infratructure (dHCI), HCI scales linearly. To add compute power or storage, you need to invest equally in both. Need more compute? Have to buy more storage – and vice versa. And, since data is copied in triple, it must cross the network three times.
With many businesses still utilizing traditional data center architecture, it will be interesting to see how the adoption of HCI and dHCI grow over the next decade. Certainly, as upgrade cycles arise and cloud migrations take place, IT leaders will be forced to reckon with tradition and the fact that technology is always changing.
Like what you read?
Contact us today to discuss data center infrastructure. Talk with our experts in a one-on-one, in-person or virtual whiteboard session. Once we have an understanding of your current architecture and deployments, we can help you to identify how to move forward and whether HCI or dHCI might be the right fit for you.
About Mindsight
Mindsight, a Chicago IT services provider, is an extension of your team. Our culture is built on transparency and trust, and our team is made up of extraordinary people – the kinds of people you would hire. We have one of the largest expert-level engineering teams delivering the full spectrum of IT services and solutions, from cloud to infrastructure, collaboration to contact center. Our customers rely on our thought leadership, responsiveness, and dedication to solving their toughest technology challenges.
Contact us at GoMindsight.com
About The Author
Siobhan Climer, Science and Technology Writer for Mindsight, writes about technology trends in education, healthcare, and business. She writes extensively about cybersecurity, disaster recovery, cloud services, backups, data storage, network infrastructure, and the contact center. When she’s not writing tech, she’s reading and writing fantasy, gardening, and exploring the world with her twin daughters. Find her on twitter @techtalksio.
How Edge Computing Will Impact The Data Center: An Infrastructure Report

 Deploying a Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
Deploying a Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
